Eight myths about snakes
... and some common misconceptions
Scales. Fangs. Venom. While snakes can make us nervous, there’s also plenty of reasons to be grateful for them.
‘Don’t walk in the long grass!’
For many, this childhood warning may be the start of a lifelong fear of Australian snakes. And while being a little wary is understandable, snakes do far more for our planet than we give them credit for.
Snakes are important. As vital predators of the food chain, these slithering superheroes keep the population of small prey species in check.
In Australia, those prey species include invasive rats and mice. Without snakes, Australia’s damaging and expensive invasive rodent problem would be far, far more destructive.
Snakes may also be gardeners! By eating prey animals that have been munching on seeds, these charismatic reptiles may even act as seed dispersers for the plant community.
But snakes aren’t just predators. They can also be prey.
As prey, the nutrients they consume can continue their journey up the food chain as they’re passed to snake-eaters such as kookaburras, hawks and goannas.
A world with snakes is a fantastic world to live in. But even so, snakes don’t have the cleanest of reputations.
We’re dispelling some common myths and misconceptions about snakes, as well as giving some tips on keeping your distance if you’d still rather they stay away.
#1. A bowl of milk will attract snakes
This is one of the more widespread beliefs, possibly originating with the Milk Snake (Lampropeltis triangulum) of North and South America.
Locals saw snakes disappearing into barns in search of rodents and believed that the snakes were drinking the milk from cows’ udders.
In fact, reptiles can’t digest dairy products and even if they could, it’s unlikely cows would stand idly by whilst being milked by a snake.
If dehydrated enough, snakes (like you) will drink just about anything, including milk.
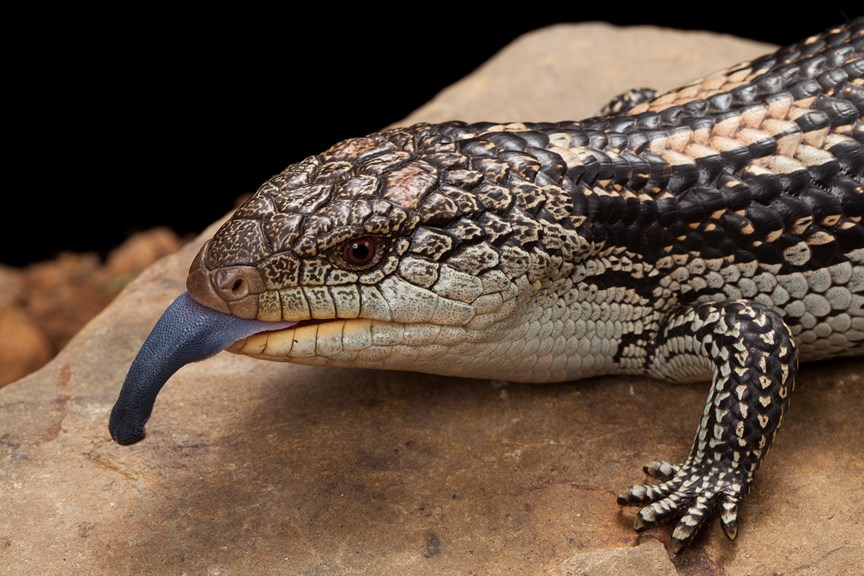
#2: Blue-tongue Lizards and Shinglebacks will discourage snakes in your garden
As a vital predator in the food chain, snakes eat frogs, lizards and even other snakes.
Some, such as the Orange-naped Snake, specialise in feeding on skinks.
Newly-hatched snakes of various species may fall prey to Blue-tongue Lizards like the one below, but as the snakes grow the reverse is usually true.
#3: If a snake’s head is cut off it will stay alive until sundown
This myth seems to be particularly popular in rural Australia.
It may be based on the fact that a snake’s body will continue to writhe for some time after decapitation, but this story is not even remotely true.
#4: A mother snake will swallow her young when threatened
Although the now-extinct Gastric-brooding Frog (Rheobatrachus species) and mouthbrooding fish are animals that appear to swallow their young, any snake ingested by another snake will immediately succumb to digestive juices.
#5: Snakes always travel in pairs
In general, the only time two snakes are in the same place is during courtship and mating.
Otherwise the larger snake will usually kill and eat the smaller one.
#6: If you kill a snake, its partner will come after you
Snakes do not have any sort of social bond, nor the intellect or memory to recognise and remember an assailant.
#7: The Hoop Snake bites onto its own tail, forms a circle and rolls down hills
Another myth common to Australia’s rural regions, but unfortunately no such snake exists.
The story is also widespread in USA and Canada where records appear from as early as the 1700s.
It may be based on the ancient Greek symbol ouroboros. The symbol depicts a serpent eating its own tail, representing constant re-creation.
#8: Snakes are deaf
Although they lack eardrums, snakes possess inner ears which can pick up not only ground-borne vibrations but low frequency airborne sounds. They do have difficulty with sounds at a higher pitch.
And now a few common misconceptions...
Snakes are cold and slimy
In fact, snake skin is dry and, depending on the surrounding temperature, can be quite warm and soft.
Snakes are poisonous
Technically snakes are venomous, not poisonous. But not all of them are venomous by any means.
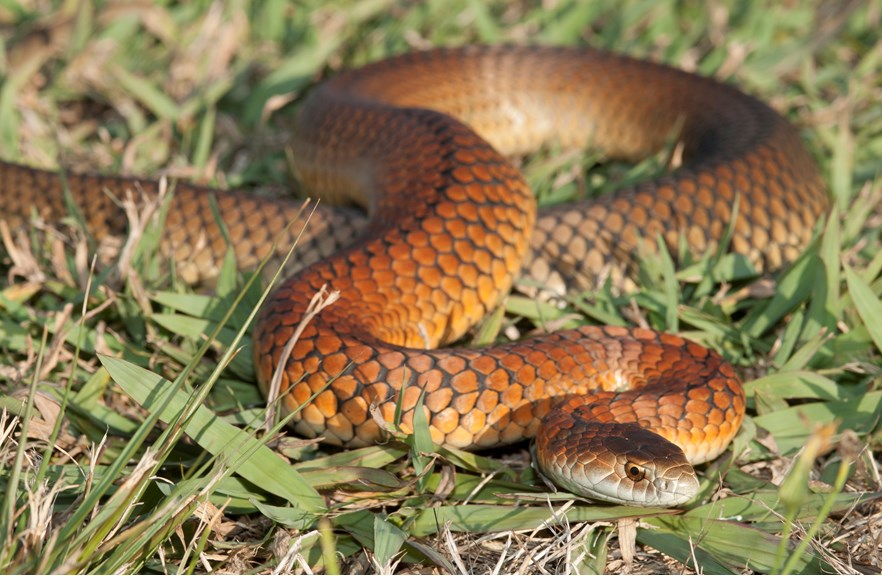
Australia has the highest proportion of venomous native snakes of any country in the world (100 out of the 140 species of land snakes), although only a handful can give a fatal bite to humans.
Poisons must be ingested, inhaled or absorbed through the skin, whilst venom must be injected into the bloodstream.
Snakes dislocate their jaws whilst feeding
Snake jawbones aren’t fused as ours are.
A highly flexible ligament joins the bones of the lower jaw, which stretch to allow enormous expansion of the mouth.
So, the mechanism is not dislocation, just great flexibility.
Pythons asphyxiate their prey by squeezing them
Recent research has shown that technically pythons kill their prey by preventing blood circulation, not breathing.
A constricting snake quickly stops the heart of its prey, and breathing fails soon afterwards.
Snakes are out to get you
Humans are larger, generally faster and stronger than Australian snakes. Snakes have a number of predators, of which humans well and truly qualify.
When you encounter a snake it is usually caught off guard (as you are), but most encounters are avoided by a snake vanishing as soon as it hears you coming.
A surprised snake will pick the nearest escape route and aim to disappear as quickly as possible, particularly when faced with a potential predator 50 times its own size.
However, snakes in general have poor eyesight and don’t always pick the best route out of trouble.
If a snake feels cornered, it will often stand and defend itself as a last resort.
Snake behaviour can also become more erratic in spring during the breeding season, and females become more defensive if eggs or young are nearby.
However, the vast majority of bites to humans in Australia occur because someone decided not to leave a snake alone.
And finally, for the record, here’s what you can do to keep snakes out of your yard
Snakes are vital to our planet’s ecosystems. That doesn’t mean we need to live with them in our homes if we’d prefer not to.
Here’s what you can do to keep snakes away from your home:
- Remove potential food sources, in this case usually rodents. Keep your property rodent-free and snakes will have less to eat.
- Remove open water sources. Snakes do find water attractive, and need to drink water regularly to survive.
- Remove shelters, such as sheets of tin on the ground and piles of rocks or firewood.
- Keep a clear area around your house. Make sure grass is cut low, remove fallen branches, and prune overgrown bushes. Most snakes prefer not to move across long stretches of open ground.
- Patch up holes in buildings. Snakes will live under houses or outbuildings where the conditions are warm and dry and can get through any gap larger than your thumb. Place wire mesh, with holes no larger than 1cm square, over all potential entry points.
Got a question about snakes? We can help you with identifications and general research. Ask us!
Discover a world 4 billion years in the making. Visit the Our Wondrous Planet exhibition at Melbourne Museum and experience the incredible connections that unite all life on Earth.